Pharmaceutical Biology
| Raffaella Filippini | Anna Piovan |
 |  |
Topic: The researches are focuses on plants as source of secondary metabolites and phytochemicals.
Current research interests:
- Biodiversity: individuate Italian endemic species and their secondary metabolite composition
- Low environmental impact experimental protocols for the extraction and phytochemical analysis
- In vitro plant cell cultures
- Biocatalysis: employement of plant cell culture enzymatic activity for the industrial synthesis of chemicals
- Pharmacognostic evaluation of herbal drugs
read more
Industries are demanding new medicinal and food ingredients for developing commercial products. In this context, wild plants may have great potential as a source of bioactive compounds. In order to find new biological resources of social and economic value, the main action is the exploration of biodiversity. The research aims to individuate Italian endemic species, in order to evaluate the secondary metabolite composition, and to establish low environmental impact experimental protocols for the extraction and phytochemical analysis.
read more
Development of systems for in vitro secondary metabolite production
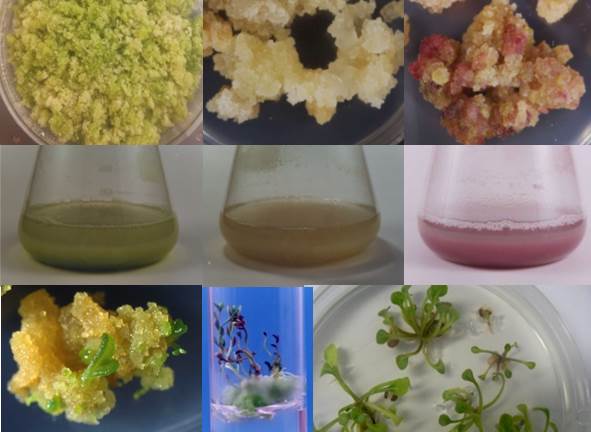
Plant cell, tissue, and organ culture is a set of techniques designed for the growth and multiplication of cells and tissues using nutrient solution in aseptic and controlled environmental conditions. This technology explores conditions that promote cell division and production of secondary metabolites to develop a potent and stable plant cell line with distinguishing features.
Micropropagation of medicinal and endangered plants
There are two strategies used for micropropagation: direct regeneration, and indirect regeneration via an intermediate callus phase. Direct regeneration without a callus phase is a reliable method for clonal propagation. Indirect regeneration often results in somaclonal variations. Whilst not recommended for conservation purposes, development of somaclones with superior characteristics has the potential for the production of useful compounds and thereby to reduce pressure on wild populations.
Biocatalysis
This technology explores enzymatic activity in plant cell culture. The use of biocatalysts for the industrial synthesis of chemicals has been attracting much attention as an environmental friendly synthetic method. Enzymes that plants produce are able to perform reactions under mild conditions (pH and temperature), with remarkable chemo-, regio-, and stereoselectivity. Due to this feature the number of biocatalysts used in organic synthesis has rapidly increased during the last decades, especially for the production of chiral compounds. Biotechnological processes using whole plant cells provide a protective environment to enzymes (e.g. in non-conventional media) and are significantly cheaper to produce than free enzymes which require several isolation and purification steps.
read more
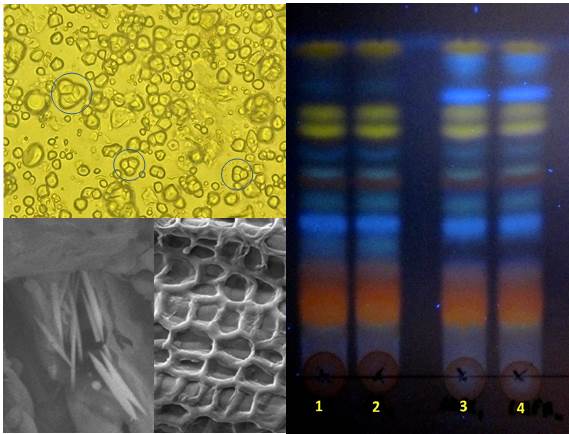
The increased request of herbal products highlights the need of improving the knowledge base for safety assessment. Safety is a fundamental principle of herbal medicines in health care and a critical component of their quality management. Correct identification and quality assurance of the starting materials are an essential prerequisite to ensure reproducible quality of herbal medicine which will contribute to its safety and efficacy. The plant material is the most important factor in manufacturing herbal products. At first, plants are inevitably “irregular” because their composition may be influenced by multiple factors. Moreover, adulteration with other material may occur by intentional or accidental substitution with similar plant species, by misidentification, and by inappropriate labeling. Although the application of regulatory standards at various stages of production, processing, and manufacturing results in quality improvement, reports on mistaken plant material, contaminants and residues, adverse effects, etc. are still present in literature.
The macro- micromorphological evaluation of herbal starting material is a crucial step, as well as the development of rapid and simple methods like TLC-densitometric analysis to obtain a phytochemical fingerprint and for semiquantitative analyses.
read more
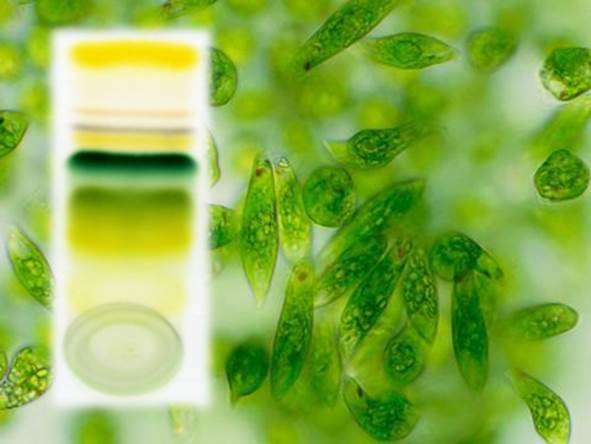
Each alga needs specific conditions to grow and these must to be defined. Research carried out aims to screen microalgae in order to evaluate their ability to accumulate high-value compounds in artificial growth environments. The research concerns the development of the proper experimental conditions with a clear impact on productivity to assess the effect of specific environmental parametersas well as the combination of several parameters at the same time.